What Color Is Used In Endospore Staining
The vegetative cells of some bacteria may put them under a great deal of stress, especially in a certain environment wherein they are deprived of nutrients such as carbon and nitrogen.
Equally a effect, they produce inactive class-endospore. This is their coping machinery for them to survive even in an unfavorable environment.
Endospore-forming leaner are commonly institute in the soil every bit well every bit in the aquatic surroundings. Some tin be institute in medical settings such equally in the example of patients with tetanus, botulism, and gas gangrene. Some of them can as well exist the reason for food poisoning. Anthrax is besides caused by endospore-forming bacteria.
A staining method for endospore was published past Dorner in 1922. In 1933, the procedure was modified by Shaeffer and Fulton. The modified process is simpler and faster. Today, the Shaeffer and Fulton method is commonly used to differentiate bacterial endospores from other vegetative cells. It is also used to differentiate spore-forming leaner from non-spore forming. (i, two, 3, and four)
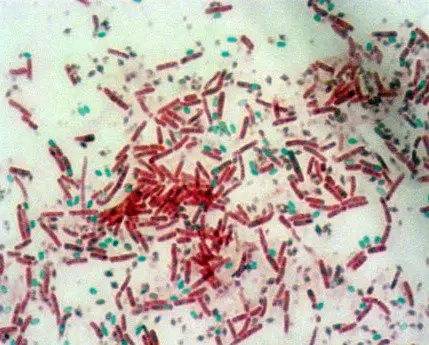
Paradigm 1: Endospore staining; a microscopic view of the cells existence studied for.
Picture Source: austincc.edu
What is the significance of endospore staining?
- It helps in classifying and differentiating bacteria.
- It is useful in the food and medicine industry, specifically in the tin industry. Information technology protects consumers by preventing food poisoning. (4, 5)
What are the principles of endospore staining?
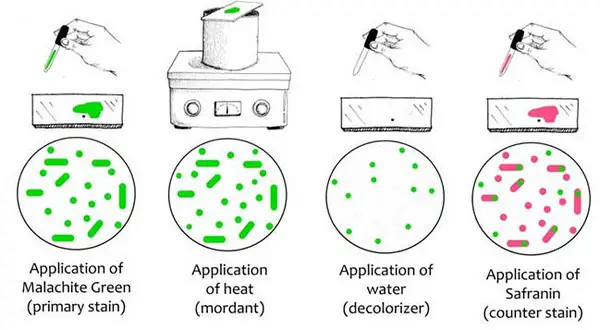
Image 2: Endospore staining procedure.
Motion-picture show Source: microbiologyinfo.com
A primary stain in the form of malachite green is used for staining endospores. It uses the heating process to act as a mordant equally endospores accept the ability to resist staining. Such a procedure does not require the use of decolorizer because malachite greenish binds to the jail cell and spore wall. The dye comes right out of the cell is washed thoroughly. However, in one case the spore wall is dyed, the color volition lock in it.
Endospores are as well resistant to de-staining. In other words, information technology has the ability to retain its primary dye even if the vegetative cells will lose the stain. To stain the decolorized vegetative cells, a counterstain should be added. One time you look at the cells nether the microscope, you will notice the following:
- The color of the vegetative cell is pinkish or carmine.
- The vegetative cells containing endospores should exist stained pink. On the other manus, the spores are viewed every bit green ellipses inside the cells.
- Mature endospores are seen as dark-green ellipses too. They are not linked with vegetative leaner. (four, 5, and six)
How is Endospore Staining done?
The staining method for endospores is done in two means: Dorner's Method staining technique (traditional method) and Schaeffer-Fulton staining technique (modified method).
#1- Schaeffer-Dulton Technique (modified method)
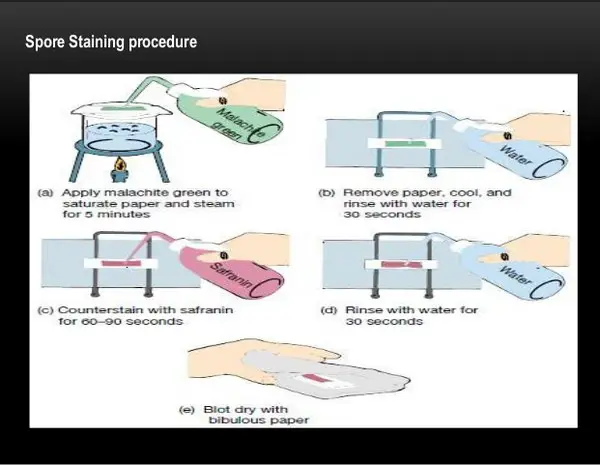
Epitome three: An endospore staining procedure using the Schaeffer-Dulton Technique.
Picture show Source: slidesharecdn.com
What do you lot need?
- Malachite green – information technology is used as the primary stain. The malachite light-green (0.5 grams) should exist dissolved in h2o (100 ml).
- Distilled h2o – information technology acts as the decolorizing agent.
- Safranin – Information technology acts equally a counterstain. (5, half-dozen, and 7)
Procedure
- Smear the sample to be studied at the center of the slide.
- Air dry the slide and heat fix.
- A blotting paper is put on the slide and the malachite greenish stain solution is pour on the slide.
- Place the slide on the heat until information technology evaporates. Boiling h2o or a Bunsen burner tin can be used to heat the slide.
- Heat, remove and re-heat the slide for about v minutes. Go on the blotting newspaper moist by adding drops of malachite green. The purpose of this step is to steam the slide and non to overheat it.
- Remove the slide and let it cool for a few minutes.
- Wash the slide. You can use distilled h2o or tap water whichever is available.
- Counterstaining is done using safranin.
- Rinse the slide and let it dry naturally.
- Examine the slide under the microscope. (6, seven, and 8)
Note: Endospores have a permeable barrier, which prevents the dye from staining the jail cell's structure. For staining to be made possible, the barrier should be destroyed kickoff.
The heat is used to destroy the bulwark and enabling the dye to interact with petodoglycan. In other words, the estrus acts as the mordant; a substance used together with the dye to completely fix in a detail textile.
Once the rut fixing is done, the next step is to wash the slide using tap or distilled water, whichever is available. The purpose of rinsing the slide with water is to decolorize the slide. Malachite greenish can be washed off easily because it weakly binds to the endospore, but in one case information technology is completely locked in the wall of the spore, information technology cannot be done off hands past water.
Endospores will retain the dye and information technology will be extremely hard to de-stain it. One time the initial washing is done, the adjacent stride is to utilize safranin, which serves equally the counterstain. It is washed to counterstain the vegetative cells. Every bit you lot notice, the colors used for primary and secondary staining are different.
Information technology is purposely washed that style so that the lab technician can hands differentiate the cells when viewing under the microscope. Nether the microscope, the vegetative cells announced ruby to pinkish in colour while the endospores are green in color when examined under the microscope. (9, 10)
#two – Dorner's Method
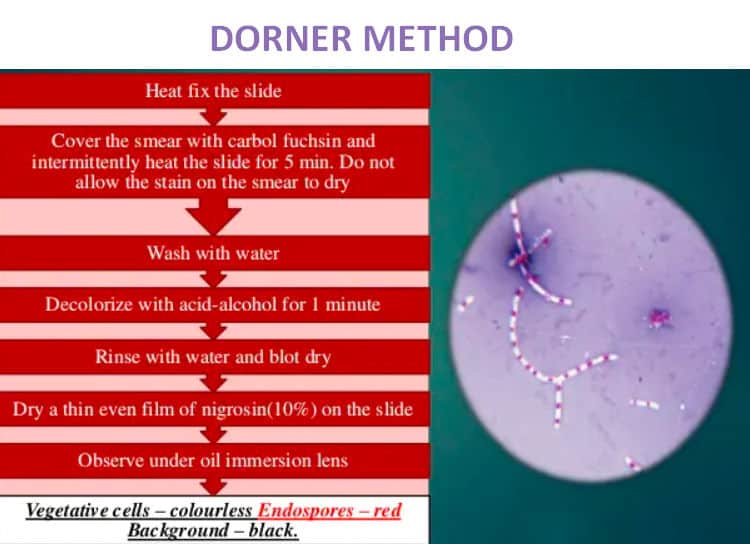
Paradigm 4: An endospore staining method using the Dorner's method.
Picture Source: generalmicroscience.com
What do you need?
- Carbolfuchsin stain
- Acrid-booze, which acts as a decolorizing agent
- Nigrosin solution, which acts as a counterstain (2, 4, and 6)
Process
- Apply a smear on the slide.
- Let the slide dry out naturally.
- Apply estrus either by boiling or using a Bunsen burner.
- Cover the smear with a blotting paper and saturate using carbolfuschin for virtually five minutes. Make sure you lot avoid overheating the slide.
- Get rid of the blotting paper and let the slide dry.
- Decolorize the slide using acid-alcohol and rinse with water.
- Counterstain by adding a drop of nigrosine.
- Allow the slide dry out.
- Examine the slide under the microscope using oil immersion. (1, 6, and 9)
Note: When examined under the microscope, the endospores appear reddish in color.
Examples of endospore stain positive organisms
- Clostridium perfringens
- C. tetani
- C. botulinum
- Bacillus cereus
- Bacillus anthracis
- Sporosarcina spp
- Desulfotomaculum spp
- Sporolactobacillus spp
Examples of endospore stain negative organisms
- Eastward. coli
- Salmonella spp (3, 6)
References
- http://www.austincc.edu/microbugz/endospore_stain.php
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endospore_staining
- https://microbeonline.com/endospore-staining-principle-process-results/
- https://microbiologyinfo.com/endospore-staining-principle-reagents-procedure-and-result/
- https://www.microscopemaster.com/endospore-stain.html
- http://spot.pcc.edu/~jvolpe/b/bi234/lab/differentialTests/endospore_stain.htm
- http://www.asmscience.org/content/education/protocol/protocol.3112
- https://courses.lumenlearning.com/microbiology/chapter/staining-microscopic-specimens/
- https://milnepublishing.geneseo.edu/suny-microbiology-lab/chapter/differential-staining-techniques/
- https://world wide web.scienceprofonline.com/microbiology/endospore-bacteria-stain-procedure.html
What Color Is Used In Endospore Staining,
Source: https://laboratoryinfo.com/endospore-staining/
Posted by: hobbsnevered1981.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Color Is Used In Endospore Staining"
Post a Comment